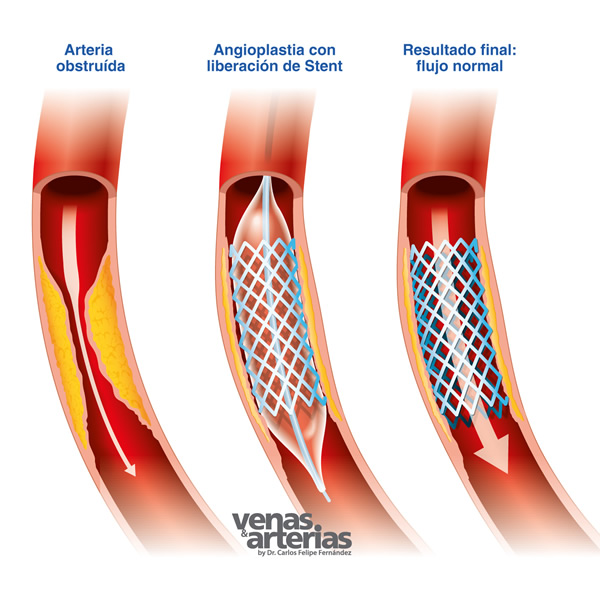
- Angioplastia
- Bypass,,en,BYPASS OR BRIDGE SURGERY,,es,Replaces Bypass,,es,graft or popliteal femoral bridge,,es,tibial femoro from pedal femoro,,ga,Bypass surgery on the leg also called bypass or femoral-popliteal bridge,,es,fémoro-tibial ó fémoro-distal,,en,in the abdomen,,es,bypass or aorto-iliac bridge or aorto-bifemoral bridge,,gl,or by extranatomic routes such as femoral-femoral bypass or axyl-bifemoral bypass,,gl,transports blood through an alternating route to the segment obstructed by arteriosclerosis,,es,as we see in the illustration on the side,,es, puente o injerto
- Endarterectomía Carotídea
- Repair or Surgery of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm,es
- Stent
Angioplastia
La Angioplastia es un procedimiento utilizado para ¨destapar¨ o ensanchar una arteria parcial o totalmente obstruida por una placa arteriosclerótica.
Se realiza en un quirófano especial llamado laboratorio de cateterismo cardíaco, a este quirófano a menudo se le llama «HEMODINAMIA», mediante una punción en la ingle o el brazo bajo anestesia local, en ocasiones combinada con una sedación suave. Una aguja es introducida en la arteria femoral a nivel de la ingle, y desde allí, under radiological control and injecting an iodinated contrast medium,,es,a small tube or catheter is advanced to the obstructed artery,,es,the femoral artery in the thigh or the coronary artery in the heart in order to dilate the obstructed segment,,es,To dilate that segment the operator inflates a balloon that is on the tip of the catheter,,es,sometimes medicated balloons are used that release drugs in order to prevent the artery from getting clogged again early,,es, se hace avanzar un pequeño tubo o catéter hasta la arteria obstruida; por ejemplo, la arteria femoral en el muslo o la coronaria en el corazón con el fin de dilatar el segmento obstruido.
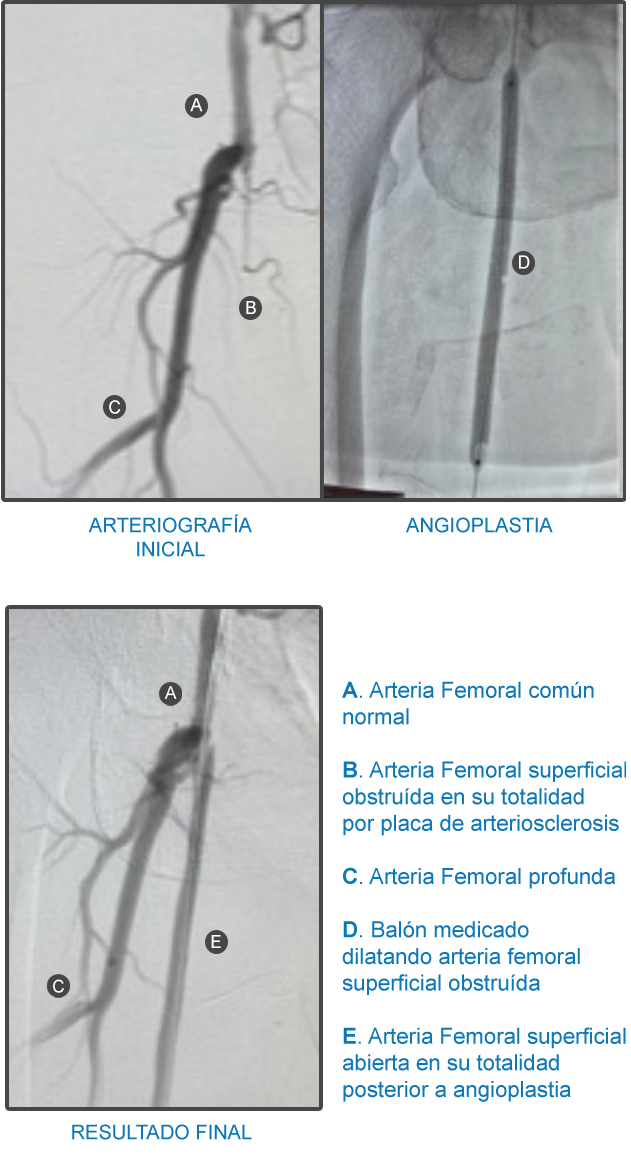
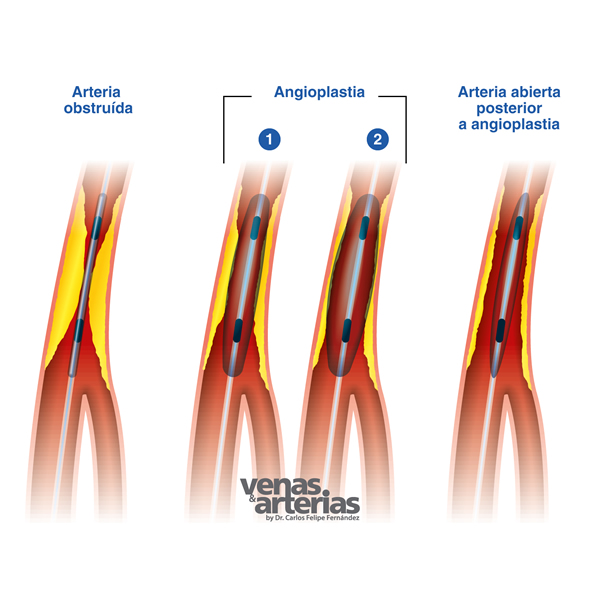
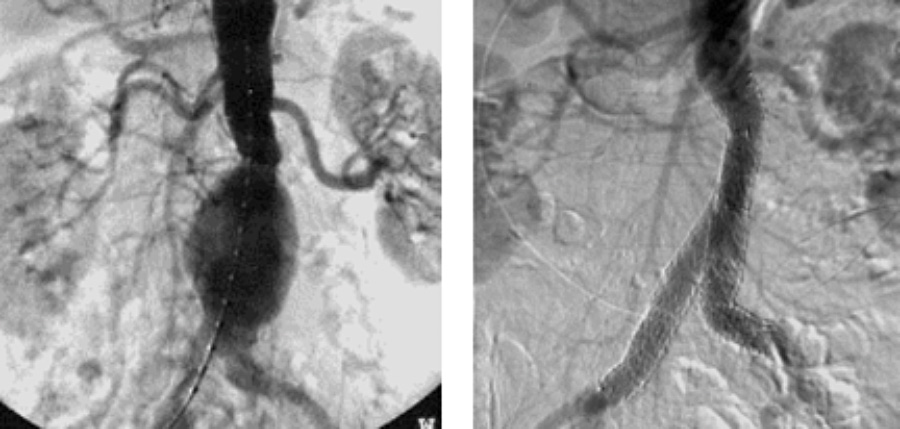
Para dilatar ese segmento el operador infla un balón que está en la punta del catéter, en ocasiones se utilizan balones medicados que liberan fármacos con el fin de evitar que la arteria se obstruya de nuevo en forma precoz, as we can see in the following arteriography where dilatation of a blocked femoral artery is evidenced using a medicated balloon,,es,Depending on the artery to be dilated,,es,as is the case of the iliac artery,,es,Angioplasty is accompanied by the release of a stent or metal mesh that holds the walls of the dilated artery to prevent re-narrowing,,es.
Dependiendo de la arteria a dilatar, como es el caso de la arteria ilíaca, la angioplastia se acompaña con la liberación de un stent o malla metálica que sostiene las paredes de la arteria dilatada para evitar su re estrechamiento.
Este procedimiento puedo lograr aliviar los síntomas de la claudicación intermitente y/o favorecer el cierre de una úlcera en el pie evitando una amputación.
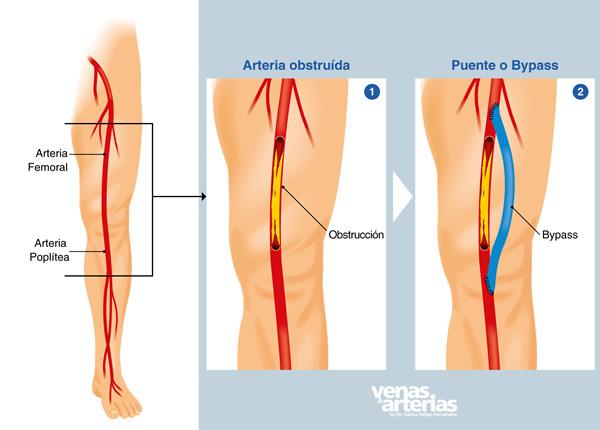
Bypass,,en,BYPASS OR BRIDGE SURGERY,,es,Replaces Bypass,,es,graft or popliteal femoral bridge,,es,tibial femoro from pedal femoro,,ga,Bypass surgery on the leg also called bypass or femoral-popliteal bridge,,es,fémoro-tibial ó fémoro-distal,,en,in the abdomen,,es,bypass or aorto-iliac bridge or aorto-bifemoral bridge,,gl,or by extranatomic routes such as femoral-femoral bypass or axyl-bifemoral bypass,,gl,transports blood through an alternating route to the segment obstructed by arteriosclerosis,,es,as we see in the illustration on the side,,es, puente o injerto
La cirugía de Bypass en la pierna también llamada bypass o puente fémoro-poplíteo, fémoro-tibial ó fémoro-distal; en el abdomen, bypass o puente aorto-ilíaco o aorto-bifemoral; o por rutas extranatómicas como en el bypass fémoro-femoral ó axilo-bifemoral, transporta la sangre por una ruta alterna al segmento obstruido por la arteriosclerosis, tal como vemos en la ilustración a un lado, the femoral artery is obstructed and a bridge or bypass transports blood through an alternating route from the femoral artery to the popliteal artery,,es,hence the name femoro-popliteus,,es,This surgery does not cure arteriosclerosis or remove the obstruction,,es,It is simply a "switch" or alternate route to transport blood beyond the obstruction and eliminate the symptoms of intermittent claudication or favor the healing of a necrotic ulcer on the foot avoiding an amputation,,es, de allí el nombre fémoro-poplíteo.
Esta cirugía no cura la arteriosclerosis o extirpa la obstrucción, sencillamente es una ¨trocha¨ o ruta alterna para transportar la sangre más allá de la obstrucción y eliminar los síntomas de la claudicación intermitente ó favorecer la cicatrización de una úlcera necrótica en el pié evitando una amputación.
The "pipeline" to be used as a bridge or "graft" can be biological,,es,belongs to the same patient,,es,such as the saphenous vein that is taken from his leg,,es,graft of choice to perform a popliteal femoro,,es,fémoro-tibial o fémoro-distal,,en,from,,ga,a synthetic graft,,es,a "pipe" of Dacron or Teflon,,es,as in the case of an aorto-bifemoral,,es,a femoral-femoral or axillo-bifemoral,,es,Usually bridges made with a vein remain permeable for a longer period than if a synthetic Dacron or Teflon pipe is used,,es, pertenece al mismo paciente, como por ejemplo la vena safena que se toma de su pierna, injerto de elección para realizar un fémoro-poplíteo, fémoro-tibial o fémoro-distal; ó, un injerto sintético, una ¨tuberia¨ de dacron o teflón, como en el caso de un aorto-bifemoral, un fémoro-femoral o un axilo-bifemoral.

Usualmente los puentes realizados con vena permanecen permeables por un lapso mayor que si se utilizare una tubería sintética de dacrón o teflón. Factors such as continuing with smoking,,es,diabetes or kidney failure,,es,they have a negative influence on the permeability of the bypass,,es, diabetes o insuficiencia renal, influyen negativamente en la permeabilidad del bypass.
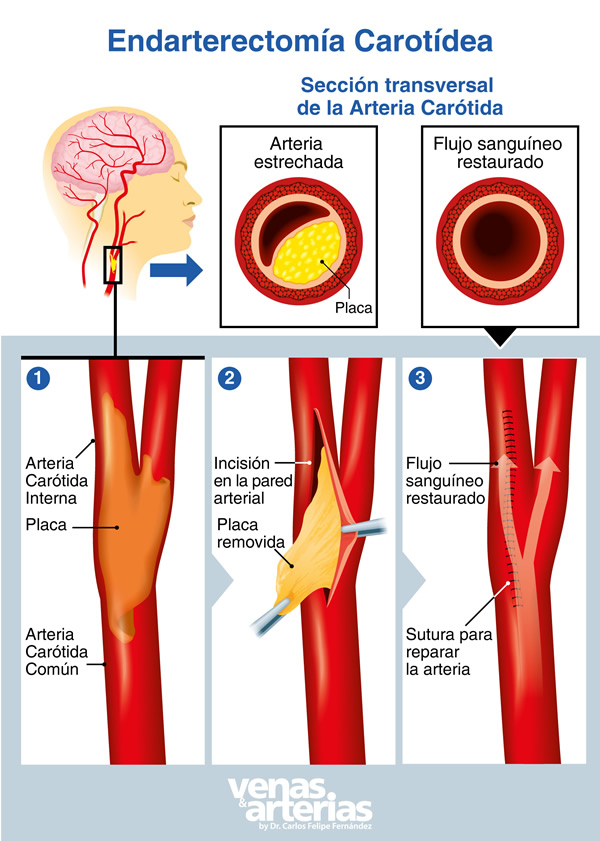
What is a carotid endarterectomy,,es,EC,,en,Carotid Endarterectomy,,gl,It is a procedure that allows the Vascular Surgeon to remove an arteriosclerotic plaque inside the carotid artery that obstructs the free flow of blood to the brain and that could fragment and produce a cerebral embolism causing a stroke.,,es,Who benefits from an EC,,es,The objective of performing an EC is to prevent a stroke,,es,It is usually indicated when the narrowing of the artery reaches the,,es ? (EC)
La Endarterectomía Carotídea (EC) es un procedimiento que permite al Cirujano Vascular remover una placa arteriosclerótica del interior de la arteria carótida que obstruye el libre tránsito de sangre hacia el cerebro y que pudiere fragmentarse y producir un embolismo cerebral causando un accidente cerebro vascular (ACV).
¿Quiénes se benefician de una EC?
El objetivo de realizar una EC es prevenir un ACV. Generalmente se indica cuando el estrechamiento de la arteria alcanza el 70 percent or more and if the narrowing may have caused,,es,A transient ischemic attack,,es,o «miniaccidente cerebrovascular»,,en,TIAs are episodes of dizziness,,es,cloudy view,,es,confusion or paralysis that may last a few minutes or up to a couple of hours,,es,A stroke characterized by vision loss,,es,or due to persistent weakness or paralysis,,es,accompanied or not by difficulty speaking,,es,The doctor may also recommend the operation even if you have not had an AIT or CVA.,,es:
- Un ataque isquémico transitorio (AIT) o «miniaccidente cerebrovascular». Los AIT son episodios de mareo, hormigueo, entumecimiento, vista nublada, confusión o parálisis que pueden durar unos pocos minutos o hasta un par de horas.
- Un ACV caracterizado por pérdida de la vista, o por debilidad o parálisis persistentes, acompañados o no por dificultad para hablar.
El médico también podría recomendarle la operación aunque no haya sufrido un AIT o ACV, if the narrowing of the carotid arteries reaches the,,es,percent or more,,es,Patients with mild obstructions,,es,percent or less,,es,typically do not need the operation,,es,How an EC is done,,es,It is done through a small incision in the skin of the lateral side of the neck that allows exposure to the carotid,,es,open it by cutting along it,,es,and place a tube,,es,shunt or shunt,,gl,in the artery,,es,above and below the obstruction,,es 80 por ciento o más.
Los pacientes con obstrucciones leves, del 50 por ciento o menos, típicamente no necesitan la operación.
¿Cómo se hace una EC?
Se realiza a través de una pequeña incisión en la piel de la cara lateral del cuello que permite exponer a la carótida, abrirla mediante un corte a lo largo de ella, y colocar un tubo (shunt o derivación ) en la arteria, por encima y por debajo de la obstrucción. The shunt allows blood to flow around the obstruction to feed the brain during the intervention,,es,Then,,es,the plate is removed,,es,it cleans,,es,the shunt is removed and the incision in the artery is closed by suturing a venous or synthetic patch,,es,from Dacron,,ro,at the site of the incision,,es,CD requires general anesthesia,,es,It lasts approximately two hours and generally involves three days of hospitalization,,es,In one or two weeks the recovery is complete,,es. A continuación, se extrae la placa, se limpia, se retira el shunt y se cierra la incisión en la arteria suturando un parche venoso o sintético (de Dacron) en el lugar de la incisión.
La EC requiere anestesia general, tiene una duración aproximada de dos horas y generalmente implica tres días de hospitalización. En una o dos semanas la recuperación es completa.
Repair or Surgery of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm,es
Los aneurismas de aorta abdominal (AAA) de menos de cinco centímetros (5 cm.) de diámetro, generalmente se monitorean con ultrasonido cada seis a doce meses, siendo de suma importancia que el paciente abandone el cigarrillo y controle muy bien su presión arterial y colesterol.
Hay dos opciones de reparación, la técnica quirúrgica convencional o Cirugía Abierta y la menos invasiva Cirugía Endovascular. La escogencia de una u otra técnica depende de varios factores, como la ubicación y tamaño del aneurisma, la edad del paciente, as well as other diseases that could coexist,,es,pulmonary emphysema,,es,renal insufficiency,,es,previous abdominal surgeries,,es,Long-term,,es,both techniques are equally effective,,es,endovascular repair being less aggressive,,es,offering a much faster recovery,,es,Open Repair or Conventional Surgery,,es,This technique involves opening the abdomen to address the aneurysm and replace the damaged segment of the aorta with a graft or synthetic duct of fabric.,,es,dacron,,en,a tube or a trouser,,ro (enfisema pulmonar, insuficiencia renal, cirugías abdominales previas). A largo plazo, ambas técnicas son igualmente efectivas, siendo la reparación endovascular menos agresiva, ofreciendo una recuperación mucho más rápida.
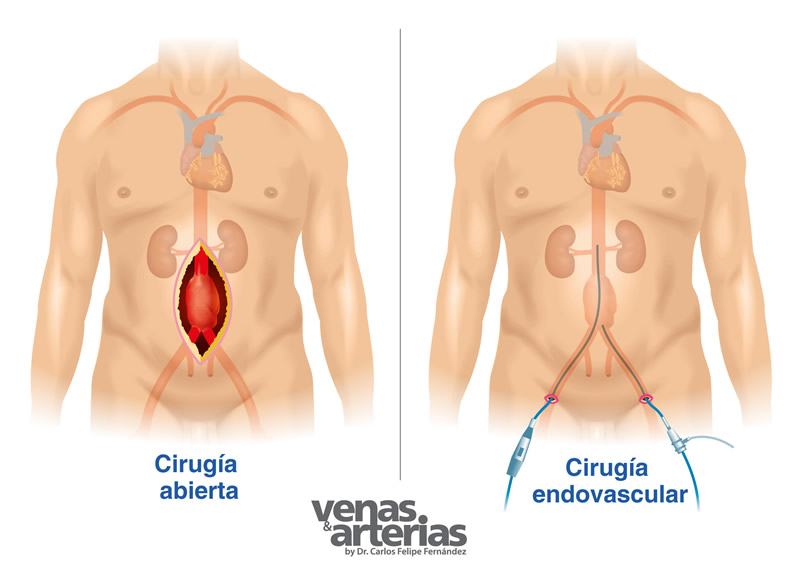
Reparación Abierta o Cirugía Convencional
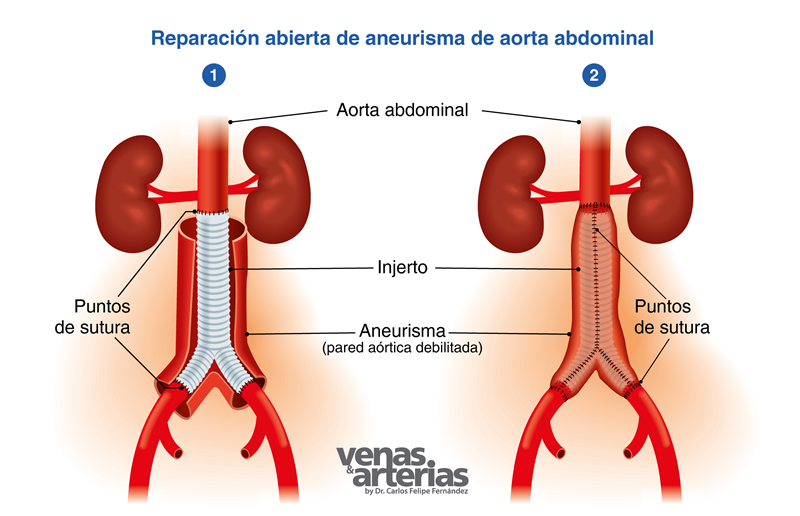
Esta técnica implica la apertura del abdomen para abordar el aneurisma y remplazar el segmento dañado de la aorta por un injerto o conducto sintético de tela (dacron), un ¨tubo¨ o un ¨pantalón¨, that is sewn in place,,es,has been present in the surgical armamentarium for almost,,es,AAA Open Surgery,,es,Abdomen open to expose aneurysm,,es,Aneurysm opening and evacuation of its contents,,es,prior circulatory arrest above and below the aneurysm,,es,c,,en,Graft in sutured pants to the healthy aorta and both iliac arteries,,es,Endovascular repair of an AAA,,es,This procedure performed for the first time in,,es,It is less invasive and increasingly popular,,es,Abdominal opening is not necessary,,es, ha estado presente en el armamentario quirúrgico desde hace casi 70 años.
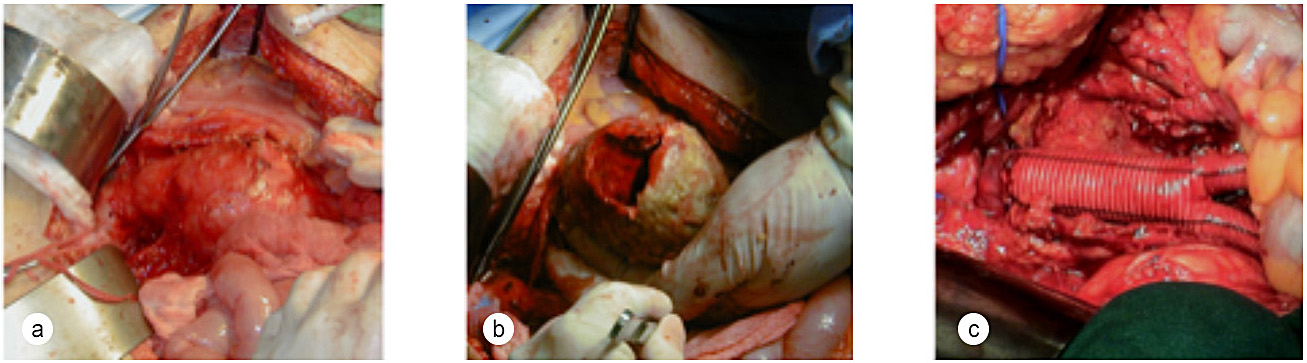
Cirugía Abierta de AAA: a) Abdomen abierto para exponer el aneurisma; b,,en,span style=,,en,font-weight,,en,strong,,en,the possibility of gangrene or leg amputation.,,es,span,,en,and accelerates atherosclerosis by decreasing arterial blood flow.,,es,p style=,,en,text-align,,en,center,,en,and these are the most likely to develop ulcers.,,es,p,,en,padding-left,,en,color,,en,blockquote,,en,span class=,,en,title,,en,a href=,,en,venasyarterias.com/masajes-prevenir-eliminar-varices-secreto-bien-guardado/,,en,target=,,en,_blank,,en,h2,,en,venasyarterias.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/Pie-diabetico.jpg,,en,rel=,,en,attachment wp-att-11256,,en,img class=,,en,wp-image-11256 alignleft,,en,src=,,en) Apertura del aneurisma y evacuación de su contenido, previo arresto circulatorio por arriba y por debajo del aneurisma; c) Injerto en pantalón suturado a la aorta sana y a ambas arterias ilíacas.
Reparación Endovascular de un AAA
Este procedimiento realizado por primera vez en 1991 es menos invasivo y cada vez es más popular. No es necesaria la apertura del abdomen. It is done through a small wound in the groin to introduce the “endograft” or “endoprosthesis”,,es,a synthetic fabric tube lined with a metal mesh that collapses and adheres to the end of another long thin tube,,es,catheter,,es,which is pushed and advanced through the femoral artery to the abdominal aorta at the site of the aneurysm,,es,is free,,ro,it expands and is fixed in place by hooks present in the metal mesh,,es,thus,,es, un tubo de tela sintética revestido de una malla metálica que va colapsado y adherido en el extremo de otro tubo largo y delgado (catéter), que se empuja y se hace avanzar a través de la arteria femoral hasta la aorta abdominal en el lugar del aneurisma, se libera, se expande y se fija en su lugar por unos ganchos presentes en la malla metálica, de esta forma, the weakened section of the aorta is reinforced from within to prevent aneurysm rupture,,es,which is excluded¨ or ¨ depressurized¨,,es,all this under radiological control and using iodized contrast,,es,Intraoperative arteriography of a case of endovascular repair of an AAA,,es,on the left the aneurysm is visualized before stent placement,,es,on the right,,es,the stent already in place and the aneurysm successfully excluded,,es,After endovascular repair,,es, el cual queda excluído¨ o ¨despresurizado¨, todo esto bajo control radiológico y utilizando contraste iodado.
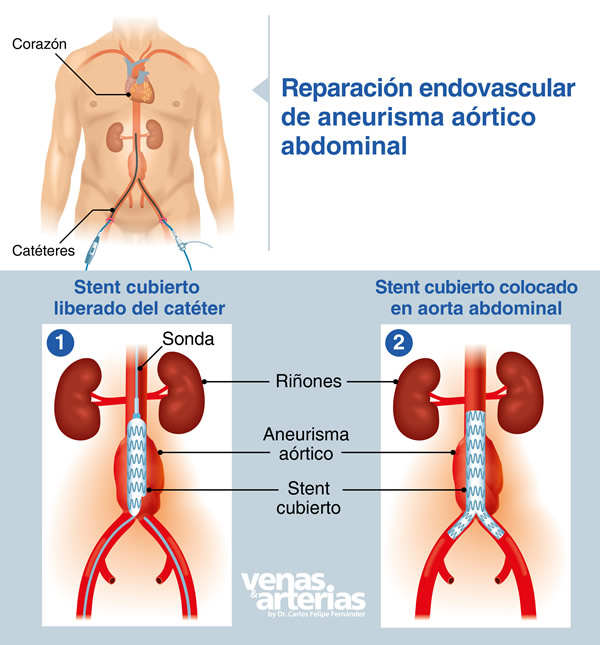
Arteriografía intraoperatoria de un caso de reparación endovascular de un AAA, a la izquierda se visualiza el aneurisma antes de la colocación de la endoprótesis, a la derecha, la endoprótesis ya en su lugar y el aneurisma exitosamente excluído.
Después de la reparación endovascular, es necesario realizar angiotomografías en forma regular para asegurar que la reparación no presenta filtraciones y que el aneurisma, en efecto, no continúe creciendo.
La Cirugía Endovascular no es una opción para todos los pacientes, aproximadamente un 40 por ciento de las personas que tienen un AAA requerirán Cirugía Abierta o convencional.
Stent
La angioplastia a menudo se combina con la colocación de un tubo de malla de alambre o stent, para ayudar a mantener la arteria abierta y disminuir la posibilidad de que vuelva a estrecharse.
Algunos stents están recubiertos con medicamentos para ayudar a mantener abierta la arteria (stents liberadores de medicamentos), mientras que otros no (stents metálicos).
El stent sostiene las paredes de la arteria para ayudar a prevenir que vuelva a estrecharse después de la angioplastia. Looks like a tiny metal mesh spring,,es,and stays inside the artery permanently to keep it open and improve blood flow,,es,The iliac artery is the site of choice for the release of a stent in order to relieve intermittent claudication,,es,that is classically manifested by pain in the gluteal region when walking,,es,particularly uphill,,es,and what improves when resting,,es,After the stent placement you may need prolonged medication treatment,,es, y queda dentro de la arteria permanentemente para mantenerla abierta y mejorar el flujo sanguíneo.
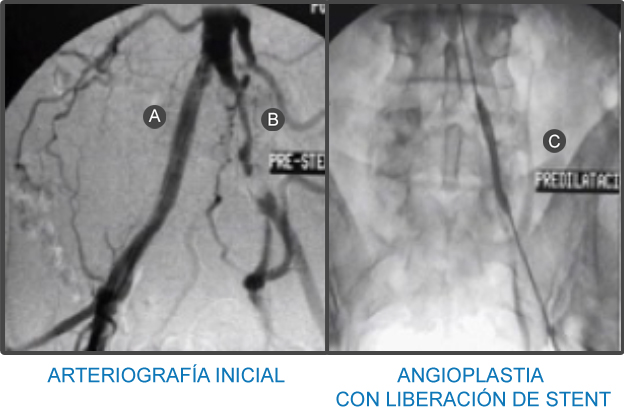
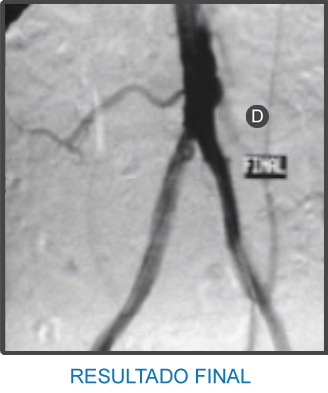

La arteria ilíaca es el sitio de elección para la liberación de un stent con el fin de aliviar la claudicación intermitente, que clásicamente se manifiesta por dolor en la región glútea al caminar, particularmente cuesta arriba, y que mejora al reposar.
Después de la colocación del stent podrías necesitar un tratamiento prolongado con medicamentos, such as aspirin or clopidogrel,,es,to reduce the likelihood of blood clots forming inside,,es,To keep your arteries healthy after angioplasty with stenting,,es,you must,,es,Give up smoking,,es,Lower your cholesterol levels,,es,keep a healthy weight,,es,Control other diseases,,es,such as diabetes or high blood pressure,,es,Exercise regularly,,es,LEGEND OF IMAGES,,es,Normal right iliac artery without arteriosclerosis,,es,B,,en,Left iliac artery completely occluded by arteriosclerosis,,es, para reducir la probabilidad de que se formen coágulos en su interior.
Para mantener tus arterias sanas después de una angioplastia con colocación de stent, debes:
- Dejar de fumar.
- Bajar tus niveles de colesterol.
- Mantener un peso saludable.
- Controlar otras enfermedades, tales como la diabetes o la presión arterial alta.
- Hacer ejercicio regularmente.
LEYENDA DE IMÁGENES
- A Arteria Ilíaca derecha normal sin arterioscleorosis.
- B Arteria Ilíaca izquierda ocluida en totalidad por arterioscleorosis.
- C Ball dilating occluded arecar,,es,Iliac artery left open in totality after angioplasty with stenting,,es.
- D Arteria Ilíaca izquierda abierta en totalidad posterior a angioplastia con colocación de stent.
